Ruby s exception hierarchy is used to differentiate between different types of errors while giving you the ability to rescue from a group of errors without specifying all of them.
Ruby rescue exception type.
The match will succeed if the exception named in the rescue clause is the same as the type of the currently thrown exception or is a superclass of that exception.
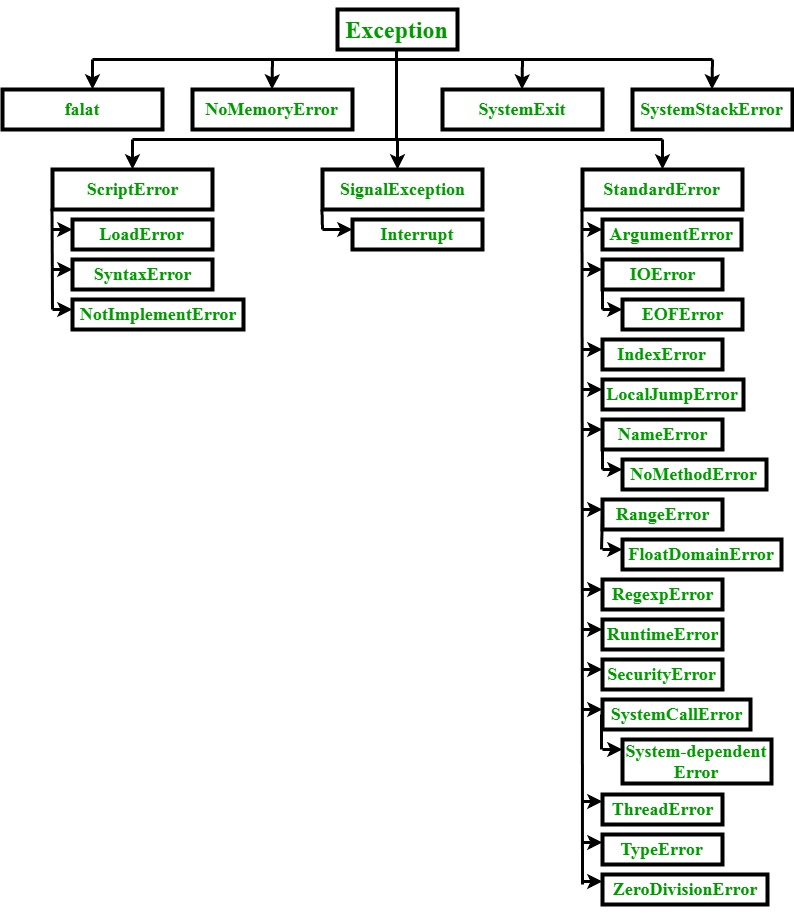
While it may be tempting to rescue every child of the exception class it is generally considered bad practice due to the way the ruby exception hierarchy is structured.
What s the right thing to do.
Ruby s exception handling mechanism is simple.
Although libraries can define their own exception subclasses the list of built in exception subclasses on ruby 2 5 looks like this.
It also uses them to handle messages from the operating system called signals if you ve ever pressed ctrl c to exit a program you ve used a signal.
For each rescue clause in the begin block ruby compares the raised exception against each of the parameters in turn.
You ve learned about errors in ruby basic exception handling the rescue begin keywords.
In this article you ll learn how to use the rescue keyword in combination with begin to handle ruby exceptions the most effective way.
The reason for this is that while all ruby exceptions and errors are an extension of the exception class many of them are reserved for use internally by ruby.
For each rescue clause in the begin block ruby compares the raised exception against each of the parameters in turn.
Exception is the root of ruby s exception hierarchy so when you rescue exception you rescue from everything including subclasses such as syntaxerror loaderror and interrupt.
At its core every ruby exception stems from a built in exception class and includes a handful of built in methods but the most commonly used exception method is message.
Ruby does require some form of begin to appear before the rescue.
The code above will rescue every exception.
The code in an else clause is executed if the code in the body of the begin statement runs to completion without.
It will be unkillable except by kill 9.
Rescuing signalexception prevents the program from responding correctly to signals.
That s because ruby uses exceptions for things other than errors.
Or i will stab you.
Become a better developer.
How to handle an exception.
The match will succeed if the exception named in the rescue clause is the same as the type of the currently thrown exception or is a superclass of that exception.
It ll break your program in weird ways.
It places the keyword rescue after any code that would probably throw an exception.
This method can be used to retrieve a specific exception message from a raised exception object.