Most operators are actually method calls.
Ruby if or operator.
Operator functions are called when the corresponding operator is used.
An operator is a symbol that represents an operation to be performed with one or more operand.
Comparison operators take simple values numbers or strings as arguments and used to check for equality between two values.
If you don t this right you won t get the expected results.
One equals sign in ruby means assignment make sure to use when you want to find out if two things are the same.
What is this funny looking ruby operator with a tilde.
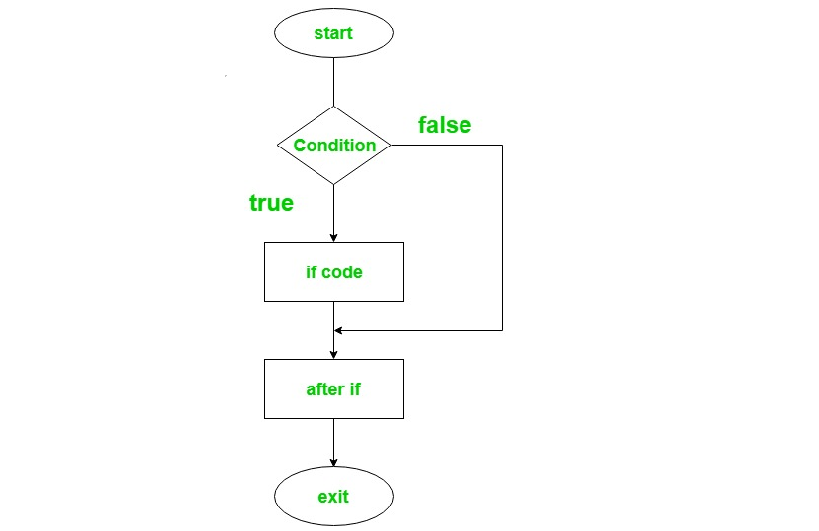
With an if statement you can check if something is true.
What is a ternary operator in ruby.
Operators are the foundation of any programming language.
B is interpreted as a plus b where the plus.
But when you want to check for the opposite not true false.
When someone tries to run 3 a it will fail.
Logical operators are used in a conditional expression for example in an if statement or in the ternary operatory we would like to combine 2 ore more conditions.
Ruby offers conditional structures that are pretty common to modern languages.
Notice that we use two equal symbols to mean equality.
For example a plus.
There are different types of operators used in ruby as follows.
Here we will explain all the conditional statements and modifiers available in ruby.
A ternary operator is made of three parts that s where the word ternary comes from.
It allows you to do a quick index search using a regular expression.
Operator overloading is not commutative that means that 3 a is not same as a 3.
It s the matching operator.
3oranges 0 9 0 this looks for numbers returns the index inside the string where the first match is found otherwise it returns nil.
These parts include a conditional statement two possible outcomes.
Method in the object referred to by variable a is called with b as its argument.
In other words a ternary gives you a way to write a compact if else expression in just one line of code.
There is a corresponding form of abbreviated assignment operator.
The operators that are words and or not are lower in the operator precedence table than the other three.
For each operator plus.